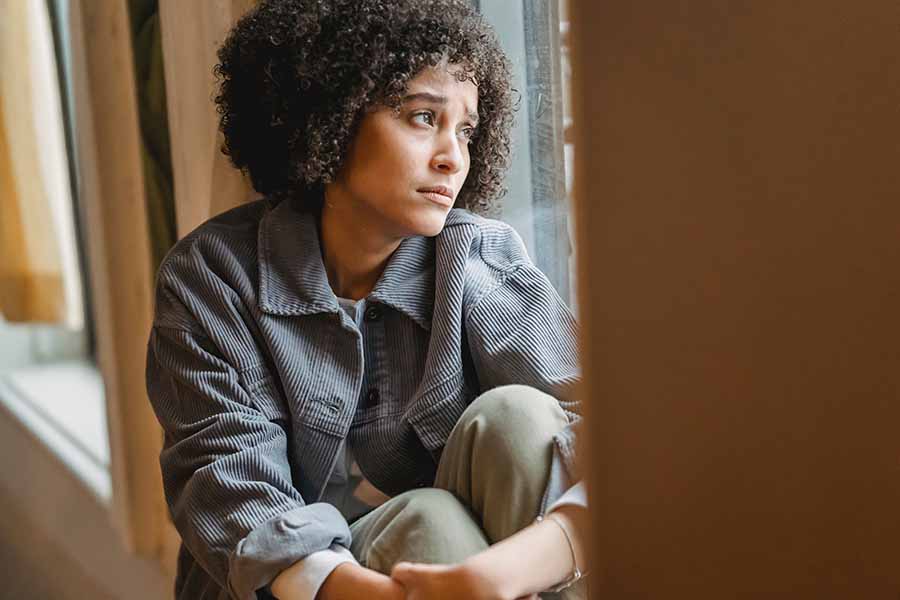
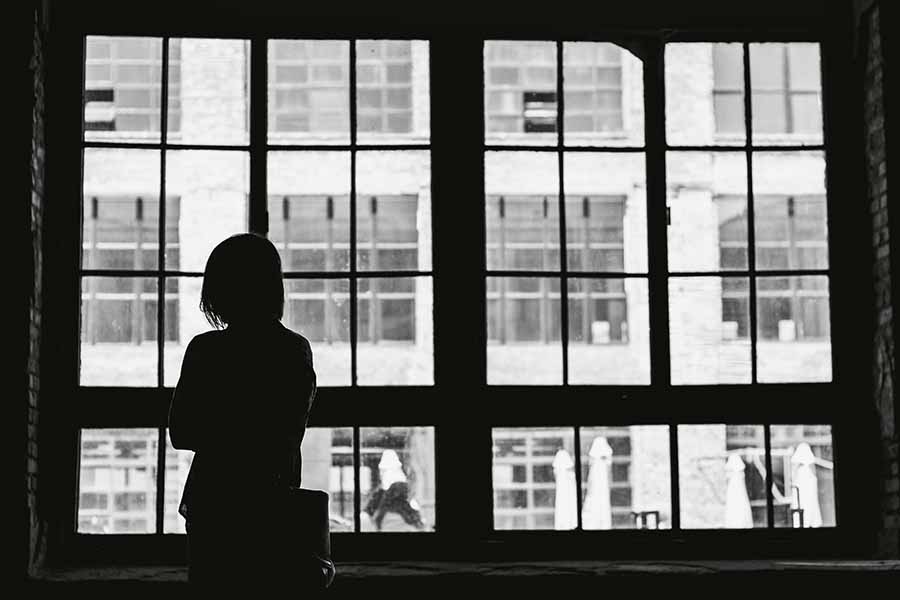
Experiencing trauma can have a profound and enduring impact on an individual’s emotional and psychological well-being. Trauma can stem from various sources, including accidents, abuse, sudden loss, or any event that overwhelms a person’s ability to cope. The effects of trauma can permeate every aspect of one’s life, manifesting as intrusive memories, nightmares, and heightened emotional reactivity.
Therapy for trauma serves as a crucial avenue for individuals to address and overcome the lasting effects of their traumatic experiences. One fundamental aspect of trauma therapy is providing a safe and confidential space for clients to explore and process their emotions, memories, and thoughts related to the traumatic event. This safe environment allows individuals to gradually open up and confront the often painful and distressing aspects of their past.
Therapists employ evidence-based approaches to trauma therapy, tailoring their methods to the unique needs of each individual. Two notable techniques mentioned are Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) and trauma-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy. EMDR involves guided eye movements that help desensitize and reprocess distressing memories, while trauma-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy aims to identify and modify negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with the trauma.
The ultimate goal of trauma therapy is to facilitate healing and empower individuals to regain control over their lives. This process involves not only alleviating distressing symptoms but also helping clients develop coping mechanisms, resilience, and a sense of empowerment. By navigating the complexities of their trauma with the support of a trained therapist, individuals can gradually reconstruct their sense of self, foster emotional resilience, and work towards reclaiming a healthier and more fulfilling life.